Bertrand Rakoto is a marketing intelligence manager for R.L. Polk. For the past decade, he’s been focused on the electric car industry and electric car services. In the first of a series of guest posts for Curbing Cars, he writes about the way people get around Paris.
By Bertrand Rakoto
Paris has a very extensive public transportation system. This might look presumptuous to begin with, but honestly, it’s quite realistic. Prior to any explanation, I must describe how the French capital city is trying to change back from cars to mass public transportation. Paris is not huge when compared to other Megacities in the world, but it’s European-big.
It’s distributed into three concentric areas. The smallest one is the inner city of Paris. A little over 2.2 million people live in the 20 administrative subdivisions (or “arrondissements”), which are shaped like a snail. When it comes to France, clichés are never very far off. The city is an expensive place to live in and numerous Parisian workers commute to downtown Paris.
However, living in the inner city is a great choice for urban lovers, with lots of cultural events, bars and clubs. And most of all, you don’t need a car when living downtown.
The second concentric area is called “Petite Couronne”. It represents 4.4 million inhabitants, divided in three departments (Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis, and Val-de-Marne). In this area, you can live without a car, but it’s more convenient to have one for weekend activities outside Paris and grocery shopping. You can avoid the daily drive for cost efficient public transportation. But in some case, it can become necessary to commute to work despite the traffic jams.
The last, largest, and third concentric area is the “Grande Couronne”. Over 5 million people live in the four remaining departments of the Ile-de-France region (being Seine-et-Marne, Yvelines, Essonne, and Val-d’Oise). In this area, a car is mandatory, or else freedom of movement is quite reduced.
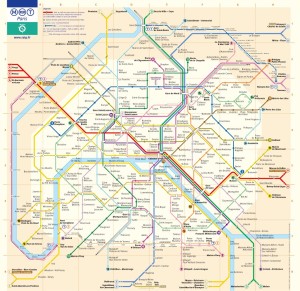
Now that you have the big picture, let’s have a look at the public transportation network.
The system is zoned, for pricing reasons. Downtown Paris is zone 1 and zone 8 is the limit of the Grande Couronne, even further away in some places. The monthly rates for Francilians (people from Ile-de-France region) depend on the number or adjacent zones they’re commuting into. There are actually 6 main types of transportation:
– The Metropolitain, a subway usually called “Métro”, the oldest, the most convenient
– The RER (Réseau Express Régional), a larger subway train that travels in all zones
– The Transilien, a real train that completes the RER network, but starts only from the six major train stations
– The Buses, the thickest and the most atomized, but fairly complicated
– The Tramway, a large kind of streetcar, which allows commuters to travel around the city limits of Paris
I began with saying the system is extensive. This listing and the map show you why. Paris’ public transit can get you anywhere in downtown Paris and most places in the Petite Couronne. And new solutions are slowly providing freedom to “car-less” people.
Those solutions are the bike sharing system (Vélib’) and the most recent is the car-sharing system (Autolib’). Next time, we’ll talk about how bike sharing and car sharing are transforming the way Parisians get around.